IsNumeric (the function we used in the previous lesson) returns TRUE if the value is a number, and FALSE, if - is not a number:
If IsNumeric(Range("A1")) = True Then 'IF VALUE IS A NUMBER...
The following code has the same effect as the previous one (we don't need to include = True because the construct itself is a condition check):
If IsNumeric(Range("A1")) = True Then 'IF VALUE IS A NUMBER...
If we want to check if a value is not a number, we can do it in two ways:
If IsNumeric(Range("A1")) = False Then 'IF VALUE IS NOT A NUMBER...
If Not IsNumeric(Range("A1")) Then 'IF THE VALUE IS NOT A NUMBER ...
Let's look at a few more functions similar to IsNumeric:
If IsDate(Range("A1")) Then 'IF VALUE IS DATE ...
If IsEmpty(Range("A1")) Then 'IF EMPTY...
If var_object Is Nothing Then 'IF THE OBJECT IS NOT DEFINED ...
To execute commands based on the type of a variable (Variant), we will need to use the VarType function.
The list of variable types will appear as soon as we enter the sign "=":
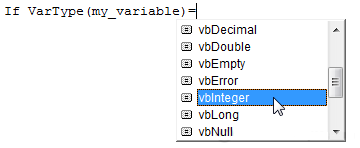
If VarType(my_variable) = vbInteger Then 'IF my_variable is of variable type Integer ...
The value of the constants:
| Constant | Value |
| vbEmpty | 0 |
| vbNull | 1 |
| vbInteger | 2 |
| vbLong | 3 |
| vbSingle | 4 |
| vbDouble | 5 |
| vbCurrency | 6 |
| vbDate | 7 |
| vbString | 8 |
| vbObject | 9 |
| vbError | 10 |
If VarType(my_variable) = vbInteger Then 'IF my_variable is an Integer variable type ... Is identical to: If VarType(my_variable) = 2 Then 'IF my_variable is an Integer variable type ...
A little earlier we used the following code snippet:
my_variable = "Example 12345" If my_variable = "Example 12345" Then ' => TRUE
In this case the two rows are the same, but if we want to check if the variable contains the value "12345" without considering other characters, we should use a command Like, and operator * (asterisk) before and after the value we are looking for.
The * operator (asterisk) stands for: any character or set of characters:
my_variable = "Example 12345" If my_variable Like "*12345*" Then ' => TRUE
The operator # (array) is decoded as: any numeric single character from 0 to 9:
my_variable = "Example 12345" If my_variable Like "Example 12###" Then ' => TRUE
Operator ? (question mark) is deciphered as: any single character:
my_variable = "Example 12345" If my_variable Like "?xample?1234?" Then ' => TRUE
We can also use specific characters or a set of characters in the same way:
my_variable = "Example 12345" If my_variable Like "[DEF]xample 1234[4-7]" Then ' => TRUE
The ! operator (exclamation point) added after the [ character will mean: any character not enclosed in square brackets:
my_variable = "Example 12345" If my_variable Like "[!GHIJ]xample 1234[!6-9]" Then ' => TRUE