Using variables we can record all types of information such as: numbers, text, date, etc.
Let's consider the first example:
Sub variables()
'Declare the variable as an integer
Dim my_variable As Integer
'Assign a certain value to the variable
my_variable = 12
'Display the value of the variable in the message window
MsgBox my_variable
End Sub
The first line of code declares a variable:
Dim my_variable As Integer
In general, declaring variables is optional and the code will work, but it is strongly recommended. This makes it easier to work with them, find them, and solve various problems. In principle, declaring variables is a good programming habit.
The type of variable indicates the nature of its content (text, number, date, etc.).
The second ribbon assigns a value to a variable:
my_variable = 12
And finally, the third ribbon displays the value of the variable in the message window:
MsgBox my_variable
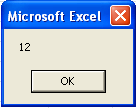
The result of executing the code will be as follows:
| Name | Type | Description | Character |
| Byte | Number | An integer between 0 and 255 | |
| Integer | Number | An integer between -32'768 and 32'767 | % |
| Long | Number | An integer between - 2'147'483'648 and 2'147'483'647 | & |
| Currency | Number | Fixed decimal number between -922'337'203'685'477.5808 and 922'337'203'685'477.5807 | @ |
| Single | Number | Floating point decimal number between -3.402823E38 and 3.402823E38 | ! |
| Double | Number | Floating point decimal number between -1.79769313486232D308 and 1.79769313486232D308 | # |
| String | Text | Text | $ |
| Date | Date | Date and Time | |
| Boolean | Boolean | True (Yes) or False (No) | |
| Object | Object | Microsoft Object | |
| Variant | Other | Any data type (default type if variable is not defined) |
Let's consider several examples with different types of variables:
'Integer
Dim nbInteger As Integer
nbInteger = 12345
'Decimal number
Dim nbComma As Single
nbComma = 123.45
'Text
Dim varText As String
varText = "moonexcel.com.ua"
'Date
Dim varDate As Date
varDate = "24.08.2012"
'Boolean value True/False
Dim varBoolean As Boolean
varBoolean = True
'Object (Worksheet as variable type)
Dim varSheet As Worksheet
Set varSheet = Sheets("Sheet2") 'Set => assignment of value to variable of type "object"
'An example of using a variable of type "object": activating a sheet
varSheet.Activate
The symbols listed in the table can be used for a shorter declaration of variables:
Dim example As Integer Dim example%
These two entries are identical.