Let's consider how we can work with the range. For this, there is a Range object in Excel, which includes both ranges of cells and one single cell. Let's see what we can do with the range.
First, let's try to select a range and define its parameters:
Sub Test2() 'moonexcel.com.ua
Dim cur_range As Range 'declare a variable of type Range
Set cur_range = Selection 'the Range object includes the selected range
display the address of the range, the number of columns and rows in the Immediate window
Debug.Print cur_range.Address
Debug.Print cur_range.Columns.Count
Debug.Print cur_range.Rows.Count
End Sub
With this code, we have assigned selected cells to our cur_range range. Next, using the Debug.Print function, the range parameters were displayed in the Immediate value preview window .
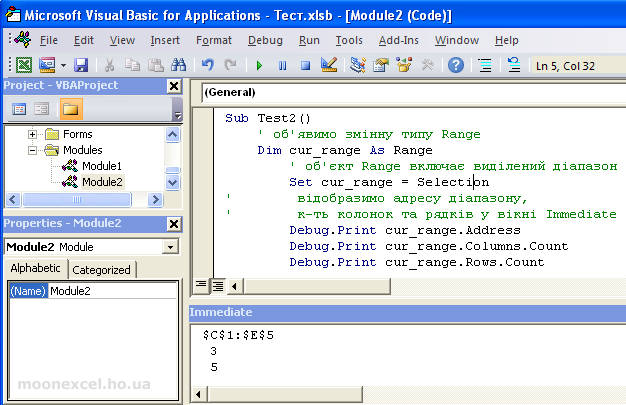
We see that the address of the range is $C$1:$E$5, the number of columns is 3, the number of rows is 5 .
Let's consider how we can highlight our range in another way. For this, we will use .UsedRange
Sub Test() 'moonexcel.com.ua
Dim cur_range As Range
Set cur_range = ActiveSheet.UsedRange
Debug.Print cur_range.Address
End Sub
The advantage of this method is that you do not need to select the range manually, Excel will do it for you, which will analyze which cells are filled in the sheet and select only them.